#Java Collection Framework
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
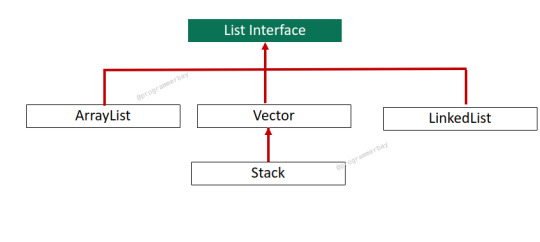
Vector Class in Java With Program Example
Vector is a collection class that implements dynamic array data structure to store elements, signifying growable array as its underlying data structure. It accepts duplicate elements and preserves insertion order. It can hold elements of different data types and allows null value. The Vector class was introduced in Java 1.2 version and is part of the original Java API. It is similar to…
View On WordPress
#collection#collection framework#Contructor of Vector#java#java program#Legacy class#List interface#Methods of Vector#Vector class
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Decode DSA with Python: Comprehensive Learning Including Python Tuple
Master Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA) with Python in this comprehensive guide. Learn key concepts step-by-step, including how Python tuples play a role in efficient coding. Whether you're preparing for coding interviews or improving your problem-solving skills, this tutorial offers practical insights and clear examples to boost your understanding of Python-based DSA. Click to read the complete guide
#bca course subjects#python tuple#Exception handling in Java#Collection framework in java#Inheritance in java#Interface in Java
0 notes
Text
okay finally colored this!
idk what the sites color theme will be, so the colors will most definitely change but for now we have a logo (ft. my oc A)
#u can just tell the type of fictional guys im into by looking at A for three seconds#tho i will try to make a variety of guys to collect and not all cutieful ones haha#i didnt feel like coding yesterday#i was locked in drawing for a comic#so i decided to hse some of that energy here#anywas coding wise!#i did a lot of research the last few days#cause i learned about frameworks#and i was like well shit#am i supposed to use them to make my website instead of doing it purely in html css and java?#and then i learned that u need to get comfortable with html css and javascript to use frameworks with little confusion#so sticking with the old fashion way#if the site gets very complicated in the far future#i might transition to frameworks#tho ik using frameworks can make websites slower oof#i went on neopets a few days back and i was shocked at how modern it looked#but god was it laggy#would like to avoid that#but yea#i will hopefully get back into coding this upcoming week#im like locked in for something else rn but ill probably have days where i dont wanna draw#boyfriend rally#web development#artists on tumblr#art#wip
1 note
·
View note
Text
Kudos on the explanation
btw ArrayList does have a .foreach() method which is a shortcut if you don't need any stream pipelines.
i fucking hate writing java dude what do you mean list.stream().forEach(list2::add)??!
syntax written by clowns
397 notes
·
View notes
Text
From 'Write Once, Run Anywhere' to Strong Security: The Java Advantage
Java, a programming language and technology ecosystem, has solidified its place in the digital world as a versatile and powerful tool. With its "Write Once, Run Anywhere" capability and an extensive array of features, Java has been instrumental in diverse domains, from mobile app development to building enterprise-level systems. This blog explores the strengths of Java, including its portability, robustness, vast ecosystem, and the thriving community that supports it. We will also discuss the value of structured training and the role of ACTE Technologies in nurturing your Java skills. By the end of this journey, you'll have a deep appreciation for the enduring excellence of Java and its role in the ever-evolving tech industry.

The Power and Versatility of Java:
1. Portability and Cross-Platform Compatibility:
Java's claim to fame, "Write Once, Run Anywhere," is not just a marketing slogan. It's a fundamental principle of Java that sets it apart. This feature is made possible by the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), which allows Java code to run on any platform that has a compatible JVM. This portability has been a game-changer, especially in a world where a diverse range of devices and operating systems coexist. Whether it's Windows, macOS, or Linux, Java applications run seamlessly, eliminating compatibility issues and reducing development time and effort.
2. Robust and Secure:
Java's architecture prioritizes robustness and security. It employs strong type checking, automatic memory management (garbage collection), and comprehensive exception handling. These features make Java code less prone to common programming errors and vulnerabilities. For businesses and organizations where system reliability and data security are critical, Java's robustness and built-in security mechanisms make it a go-to choice. Critical systems, such as banking applications, rely on Java to ensure the highest level of protection against errors and threats.
3. Vast Ecosystem:
The Java ecosystem is vast and varied. It includes an extensive library of classes, frameworks, and tools that cater to a wide range of application development needs. Some of the notable components of this ecosystem include:
Java Standard Library: Java's standard library provides a wealth of pre-built classes and utilities for common programming tasks, simplifying development.
Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB): For enterprise-level applications, EJB offers a framework for building scalable, distributed, and transactional components.
JavaServer Pages (JSP) and Servlets: These technologies enable the development of dynamic web applications, making Java a popular choice for web development.
Spring Framework: Spring is a comprehensive framework for building enterprise-level applications, offering features like dependency injection, aspect-oriented programming, and more.
Android Development: Java serves as the primary language for developing Android mobile applications, further expanding its reach.
4. Community and Support:
Java's success is not only due to its technical prowess but also its thriving community of developers, enthusiasts, and experts. This community-driven approach ensures that Java remains relevant, up-to-date, and aligned with industry best practices. Developers can find a wealth of resources, forums, and collaborative environments where they can learn, share knowledge, and solve challenges. The community's collective wisdom and problem-solving spirit have contributed to the continuous evolution of Java.

Java's enduring excellence is a testament to its portability, robustness, vast ecosystem, and strong community support. If you're looking to harness the potential of Java and embark on a journey of learning and mastery, consider exploring the Java training programs offered by ACTE Technologies. With dedication and the right resources, you can leverage Java's capabilities and contribute to the ever-evolving tech landscape.
Java has stood the test of time, offering unparalleled portability, robustness, a rich ecosystem, and a vibrant community. Whether you're building enterprise-level applications or dynamic web services, Java remains a reliable choice. ACTE Technologies' structured training can help you unlock the full potential of Java, enabling you to thrive in the dynamic tech industry.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
java full stack
A Java Full Stack Developer is proficient in both front-end and back-end development, using Java for server-side (backend) programming. Here's a comprehensive guide to becoming a Java Full Stack Developer:
1. Core Java
Fundamentals: Object-Oriented Programming, Data Types, Variables, Arrays, Operators, Control Statements.
Advanced Topics: Exception Handling, Collections Framework, Streams, Lambda Expressions, Multithreading.
2. Front-End Development
HTML: Structure of web pages, Semantic HTML.
CSS: Styling, Flexbox, Grid, Responsive Design.
JavaScript: ES6+, DOM Manipulation, Fetch API, Event Handling.
Frameworks/Libraries:
React: Components, State, Props, Hooks, Context API, Router.
Angular: Modules, Components, Services, Directives, Dependency Injection.
Vue.js: Directives, Components, Vue Router, Vuex for state management.
3. Back-End Development
Java Frameworks:
Spring: Core, Boot, MVC, Data JPA, Security, Rest.
Hibernate: ORM (Object-Relational Mapping) framework.
Building REST APIs: Using Spring Boot to build scalable and maintainable REST APIs.
4. Database Management
SQL Databases: MySQL, PostgreSQL (CRUD operations, Joins, Indexing).
NoSQL Databases: MongoDB (CRUD operations, Aggregation).
5. Version Control/Git
Basic Git commands: clone, pull, push, commit, branch, merge.
Platforms: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket.
6. Build Tools
Maven: Dependency management, Project building.
Gradle: Advanced build tool with Groovy-based DSL.
7. Testing
Unit Testing: JUnit, Mockito.
Integration Testing: Using Spring Test.
8. DevOps (Optional but beneficial)
Containerization: Docker (Creating, managing containers).
CI/CD: Jenkins, GitHub Actions.
Cloud Services: AWS, Azure (Basics of deployment).
9. Soft Skills
Problem-Solving: Algorithms and Data Structures.
Communication: Working in teams, Agile/Scrum methodologies.
Project Management: Basic understanding of managing projects and tasks.
Learning Path
Start with Core Java: Master the basics before moving to advanced concepts.
Learn Front-End Basics: HTML, CSS, JavaScript.
Move to Frameworks: Choose one front-end framework (React/Angular/Vue.js).
Back-End Development: Dive into Spring and Hibernate.
Database Knowledge: Learn both SQL and NoSQL databases.
Version Control: Get comfortable with Git.
Testing and DevOps: Understand the basics of testing and deployment.
Resources
Books:
Effective Java by Joshua Bloch.
Java: The Complete Reference by Herbert Schildt.
Head First Java by Kathy Sierra & Bert Bates.
Online Courses:
Coursera, Udemy, Pluralsight (Java, Spring, React/Angular/Vue.js).
FreeCodeCamp, Codecademy (HTML, CSS, JavaScript).
Documentation:
Official documentation for Java, Spring, React, Angular, and Vue.js.
Community and Practice
GitHub: Explore open-source projects.
Stack Overflow: Participate in discussions and problem-solving.
Coding Challenges: LeetCode, HackerRank, CodeWars for practice.
By mastering these areas, you'll be well-equipped to handle the diverse responsibilities of a Java Full Stack Developer.
visit https://www.izeoninnovative.com/izeon/
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Software Development: Essential Terms for Beginners to Know
Certainly, here are some essential terms related to software development that beginners, including software developers in India, should know:
Algorithm: A step-by-step set of instructions to solve a specific problem or perform a task, often used in programming and data processing.
Code: The written instructions in a programming language that computers can understand and execute.
Programming Language: A formal language used to write computer programs, like Python, Java, C++, etc.
IDE (Integrated Development Environment): A software suite that combines code editor, debugger, and compiler tools to streamline the software development process.
Version Control: The management of changes to source code over time, allowing multiple developers to collaborate on a project without conflicts.
Git: A popular distributed version control system used to track changes in source code during software development.
Repository: A storage location for version-controlled source code and related files, often hosted on platforms like GitHub or GitLab.
Debugging: The process of identifying and fixing errors or bugs in software code.
API (Application Programming Interface): A set of protocols and tools for building software applications. It specifies how different software components should interact.
Framework: A pre-built set of tools, libraries, and conventions that simplifies the development of specific types of software applications.
Database: A structured collection of data that can be accessed, managed, and updated. Examples include MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB.
Frontend: The user-facing part of a software application, typically involving the user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design.
Backend: The server-side part of a software application that handles data processing, database interactions, and business logic.
API Endpoint: A specific URL where an API can be accessed, allowing applications to communicate with each other.
Deployment: The process of making a software application available for use, typically on a server or a cloud platform.
DevOps (Development and Operations): A set of practices that aim to automate and integrate the processes of software development and IT operations.
Agile: A project management and development approach that emphasizes iterative and collaborative work, adapting to changes throughout the development cycle.
Scrum: An Agile framework that divides work into time-boxed iterations called sprints and emphasizes collaboration and adaptability.
User Story: A simple description of a feature from the user's perspective, often used in Agile methodologies.
Continuous Integration (CI) / Continuous Deployment (CD): Practices that involve automatically integrating code changes and deploying new versions of software frequently and reliably.
Sprint: A fixed time period (usually 1-4 weeks) in Agile development during which a specific set of tasks or features are worked on.
Algorithm Complexity: The measurement of how much time or memory an algorithm requires to solve a problem based on its input size.
Full Stack Developer: A developer who is proficient in both frontend and backend development.
Responsive Design: Designing software interfaces that adapt and display well on various screen sizes and devices.
Open Source: Software that is made available with its source code, allowing anyone to view, modify, and distribute it.
These terms provide a foundational understanding of software development concepts for beginners, including software developers in India.
#software app#software development#software developers#software development in India#Indian software developers
3 notes
·
View notes
Text
Mastering REST API Testing: Automation with Rest Assured and Postman

If you’ve ever wondered how web and mobile apps exchange data behind the scenes, you're already halfway to understanding the power of REST APIs. They’re the invisible gears that keep modern software running smoothly. But how do developers and testers ensure these APIs are working as expected?
Enter REST API testing—an essential skill for any aspiring or experienced tester. And if you're serious about becoming an expert in this space, mastering tools like Rest Assured and Postman is your best first step.
Whether you're new to automation or already working in QA, this guide will help you understand why REST API testing is so crucial, and how you can automate it efficiently. We’ll also show you how to start your journey with the right learning resource.
What is REST API Testing?
Let’s break it down:
REST (Representational State Transfer) is a widely used architectural style for designing networked applications. APIs following this model—known as RESTful APIs—use standard HTTP methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE.
Testing these APIs means ensuring that they’re functioning as intended—delivering the right data, working under different conditions, and responding appropriately to errors.
In simple terms: REST API testing helps developers and testers confirm that APIs are reliable, secure, and performing as expected—before they reach the hands of users.
Why Should You Automate REST API Testing?
Manual testing can only take you so far. Imagine having to manually test every API endpoint, every time you make a change in code—it’s slow, inefficient, and error-prone.
That’s where REST API automation testing comes in.
Automation ensures:
Faster testing cycles
Consistent and repeatable results
Easy integration into CI/CD pipelines
Early bug detection
Improved test coverage
And most importantly—it frees up your time, allowing you to focus on more complex testing challenges.
Two Tools You Need: Rest Assured and Postman
1. Postman – The API Explorer
Postman is a GUI-based tool that lets you send HTTP requests to APIs and inspect their responses. It’s incredibly user-friendly, making it a favorite among testers and developers for quick API validation.
You can use it to:
Create and run manual tests
Write automated test scripts using JavaScript
Set up collections for test suites
Generate and share API documentation
If you’re just starting, Postman is the perfect gateway into the world of REST API testing.
2. Rest Assured – The Automation Powerhouse
Rest Assured is a Java-based library that allows you to write powerful and flexible API tests using code. It integrates well with testing frameworks like TestNG and JUnit, and it’s perfect for embedding into your CI/CD pipelines.
Why Rest Assured stands out:
Supports BDD (Behavior-Driven Development)
Easily handles JSON and XML responses
Offers in-depth assertions for response validation
Can automate authentication flows, headers, parameters, etc.
When you pair Postman with Rest Assured, you’ve got a complete testing toolbox—manual + automated.
Who Should Learn REST API Testing?
You might be wondering: Is this right for me?
If you fall under any of these categories, the answer is yes:
Manual testers looking to transition into automation
Automation testers expanding their skillset
Developers who want to test their own APIs
QA professionals involved in Agile or DevOps teams
Beginners entering the testing field
The good news is: you don’t need to be a coding wizard to get started. With the right guidance and structured learning path, anyone can master this.
Learn REST API Testing (Automation) From Scratch – With the Right Course
Learning on your own can be overwhelming. You might find scattered YouTube videos, outdated blog posts, or complex documentation.
What you need is a step-by-step course that takes you from beginner to expert.
We highly recommend checking out this complete learning experience: 👉 Rest API Testing (Automation) : Rest Assured + PostMan
This course has everything:
Beginner-friendly intro to APIs and HTTP methods
Real-world Postman projects
In-depth Rest Assured automation scripting
Integration with TestNG, Maven, and reporting tools
Hands-on assignments and practical demos
Interview preparation and tips
It’s perfect for both beginners and professionals, and it’s designed to help you build a strong portfolio while preparing for real job interviews.
Key Topics Covered in the Course
Here’s a peek at what you’ll learn:
What is an API and how REST works
Understanding API endpoints, methods, headers, and responses
Postman interface: Collections, environments, and variables
Writing test scripts in Postman using JavaScript
Building REST API automation frameworks using Rest Assured
Validating JSON and XML responses
Working with OAuth2 and authentication mechanisms
Advanced concepts like request chaining and data-driven testing
CI/CD integration for API tests
By the end of the course, you’ll be confident in your ability to automate API testing workflows like a pro.
Real-World Benefits of API Automation Testing
Let’s talk outcomes. What do you really gain from mastering API testing?
✅ Better Job Prospects
Automation testers with API testing skills are highly in-demand across tech companies, especially those using Agile and DevOps.
✅ Efficient Testing Process
Manual testing can be slow and repetitive. API automation saves hours and reduces human error—making your testing more efficient.
✅ Stronger Test Coverage
You’ll be able to test deep application layers that aren’t always accessible via UI testing. This leads to more thorough test coverage.
✅ Seamless CI/CD Integration
Automated API tests are easy to plug into your CI/CD pipeline, ensuring faster releases and fewer bugs in production.
✅ Improved Confidence in Software Quality
By validating the core logic of your application through API testing, you ensure robust, scalable, and bug-free applications.
Career Opportunities After Learning REST API Automation
The demand for skilled API testers continues to grow as companies shift toward microservices and cloud-based architectures. Here are some roles where your new skills will shine:
QA Automation Engineer
Software Development Engineer in Test (SDET)
Test Automation Architect
API Test Consultant
DevOps QA Engineer
You’ll also be able to crack interviews with top companies by showcasing your practical experience and understanding of REST API testing tools and techniques.
Tips for Getting Started
Ready to take the plunge? Here are some quick tips:
Start with Postman – It’s simple, visual, and gives you a feel for how APIs work.
Gradually move to Rest Assured – Once you’re confident with Postman, start writing automation scripts.
Work on small real-world projects – Test open-source APIs or mock your own.
Take notes and track your progress – This helps you retain and revise better.
Enroll in a structured course like this one: 👉 Rest API Testing (Automation) : Rest Assured + PostMan It guides you step-by-step with hands-on projects and real-world context.
Final Thoughts
In today’s software world, REST API testing is not optional—it’s essential. Whether you're working on web, mobile, or cloud apps, you need to ensure your APIs are rock-solid.
By mastering tools like Postman and Rest Assured, you equip yourself with the skills that make you stand out in the job market, deliver better-quality software, and future-proof your career in testing.
You don’t have to figure it all out on your own. Take the smart route and learn with expert guidance. Start your journey today with this comprehensive and practical course: 👉 Rest API Testing (Automation) : Rest Assured + PostMan
Automation is the future—and your journey begins now. 🚀
0 notes
Text
ArrayList Class in Java With Program Example
Arraylist is a child class of AbstractList and implements List interface. It represents dynamic array that can grow or shrink as needed. In case of standard array, one must know the number of elements about to store in advance. In other words, a standard array is fixed in size and its size can’t be changed after its initialisation. To overcome this problem, collection framework provides…

View On WordPress
#arraylist#collection#collection framework#Hierarchy in Collection Framework#java#java program#List interface
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Master Polymorphism in Java – Scientech Easy
Dive into Polymorphism in Java with easy-to-follow guides at Scientech Easy. Learn how Java supports method overloading and overriding, enabling flexible and dynamic behavior in your programs. Perfect for enhancing your OOP skills!

#constructor in java#collection framework in java#Exception handling in Java#inheritance in java#Interface in Java#Python tuple#bca course subjects
0 notes
Text
Core Java Training coaching center in chennai
The best Core Java training coaching centers in Chennai offer well-structured courses covering all key aspects of Java programming. These include Java basics, object-oriented programming (OOP), exception handling, multithreading, collections framework, Java Input/Output (I/O), and Java Development Kit (JDK) tools.
0 notes
Text
Why Is Java Secure For Web Applications Today?
Java is considered one of the most secure programming languages for web applications due to its robust architecture, strong memory management, and built-in security features. It runs inside the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), which adds an extra layer of abstraction between the application and the underlying hardware, making it harder for malicious code to directly access system resources. Java also offers features like automatic garbage collection, exception handling, and strong type-checking, which reduce the chances of memory leaks and buffer overflow vulnerabilities common issues that can be exploited in other languages.
Additionally, Java provides a comprehensive security API that includes cryptography, authentication, access control, and secure communication. Frameworks like Spring Security further enhance security by enabling features such as role-based access control, CSRF protection, and OAuth2 authentication with minimal configuration. The large and active Java developer community regularly identifies and patches vulnerabilities, ensuring continuous updates and security enhancements.
Because of these features, Java remains a reliable choice for building secure, scalable, and maintainable web applications in enterprise environments.
To understand these principles in-depth, you may explore a full stack Java developer course.
0 notes
Text
From Beginner to Expert: Mastering Java Programming
Commencing a Java learning journey involves planning, commitment, and disciplined study. In this guide, we will explore a comprehensive roadmap to effectively learn Java, equipping you with the skills and knowledge needed to become proficient in this versatile programming language.

Navigating the Path to Java Mastery:
Grasping Fundamentals: Before delving into Java, it's essential to grasp the fundamental concepts of programming. Start by familiarizing yourself with variables, data types, control structures, and basic algorithms. These foundational principles lay the groundwork for understanding Java's syntax and language features.
Setting Up Your Environment: To begin coding in Java, you'll need to set up your development environment. Install the Java Development Kit (JDK) and choose an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) such as Eclipse or IntelliJ IDEA. These tools provide essential features like syntax highlighting and debugging tools to streamline your coding experience.
Mastering Syntax and Object-Oriented Concepts: Dive into Java syntax and object-oriented programming (OOP) concepts, including classes, objects, methods, inheritance, polymorphism, encapsulation, and abstraction. Understanding these concepts is crucial for writing efficient and maintainable Java code.
Exploring Core Libraries: Java offers a robust set of core libraries that provide essential functionality for various tasks. Explore libraries such as java.lang, java.util, and java.io, which offer classes and methods for common operations like string manipulation, input/output operations, and collection manipulation.

Hands-On Practice: Practice is key to mastering Java programming. Start by writing simple programs and gradually tackle more complex challenges. Participate in coding competitions, solve coding puzzles, and work on projects to apply your knowledge in real-world scenarios.
Understanding Java APIs and Frameworks: Familiarize yourself with Java APIs and frameworks that simplify development tasks. Explore APIs for GUI development, database connectivity, web development, and more. Additionally, delve into popular Java frameworks like Spring and Hibernate, which offer reusable components and design patterns for building robust applications.
Building Projects: Project-based learning is an effective way to solidify your Java skills. Start with small projects and gradually tackle larger ones as you gain confidence. Building projects allows you to apply your knowledge in practical scenarios and enhance your problem-solving skills.
Continuous Learning and Growth: Java is a constantly evolving language, so commit to continuous learning and growth. Stay updated with the latest Java features, best practices, and industry trends. Join Java communities, attend webinars, and participate in online forums to connect with fellow developers and expand your knowledge.
Conclusion:
Mastering Java is an enriching journey that offers endless opportunities in software development. By following this roadmap, you can build a strong foundation in Java programming and unlock your full potential as a developer. Remember to stay curious, embrace challenges, and enjoy the process of learning and growing as a Java programmer. With dedication and perseverance, you can achieve proficiency in Java and embark on a fulfilling career in software development.
#java course#javascript#javaprogramming#programming#computerscience#computerengineering#programminglanguage#tech#technology#training#java training#java training course
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Java Interview Questions and Answers: Your Ultimate Preparation Guide

That’s why we’ve created "Java Interview Questions and Answers: Your Ultimate Preparation Guide" to help you get fully prepared and stand out from the competition.
Java remains one of the most widely used programming languages across the tech industry. From building enterprise-grade applications to Android development and cloud-based systems, Java is a powerful, object-oriented language that has stood the test of time. As a result, Java continues to be a core requirement in thousands of job listings globally, and technical interviews often focus heavily on Java fundamentals, coding practices, and real-world problem-solving.
This guide offers a comprehensive breakdown of the most commonly asked Java interview questions, along with expert-level answers that explain not just the what, but the why—helping you build a strong conceptual foundation.
Why This Guide Matters
"Java Interview Questions and Answers: Your Ultimate Preparation Guide" is designed to equip you with the most relevant, up-to-date, and frequently asked questions across various job roles and experience levels. Whether you're a fresher just entering the field or a seasoned Java developer with years of experience, the questions included in this guide cover all the core areas expected in a Java interview.
With structured answers, real-world examples, and technical explanations, this guide helps you understand each topic in depth—so you’re not just memorizing, but truly learning.
Key Topics Covered in This Guide
Here are the primary categories of Java interview questions and answers covered in this ultimate preparation guide:
1. Core Java Basics
These questions test your fundamental knowledge of Java, including syntax, control structures, and data types. Examples include:
What are the main features of Java?
What is the difference between JDK, JRE, and JVM?
Explain the concept of platform independence in Java.
2. Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in Java
As Java is built around the OOP paradigm, interviewers often assess your grasp of these principles:
What is encapsulation, and why is it important?
Explain inheritance with examples.
What is polymorphism, and how is it implemented in Java?
3. Exception Handling
Proper exception handling is critical in robust Java applications. Common questions include:
What is the difference between checked and unchecked exceptions?
How do try, catch, finally, and throw work together?
What is the purpose of custom exceptions?
4. Collections Framework
This is a favorite topic in Java interviews due to its practical importance:
What is the difference between ArrayList and LinkedList?
How does HashMap work internally?
What are the differences between Set, List, and Map?
5. Multithreading and Concurrency
Java supports concurrent programming, and questions in this category test your knowledge of threading concepts:
What is a thread in Java?
Explain the differences between Runnable and Thread.
How do you avoid thread-safety issues in Java applications?
6. Java 8 and Beyond
Modern Java versions introduced features like lambdas, streams, and functional programming:
What are lambda expressions?
How do you use the Stream API in Java 8?
What is the difference between Optional and null?
7. JVM Internals and Memory Management
Senior-level candidates are often expected to understand how Java works under the hood:
How does garbage collection work in Java?
What are the different memory areas in JVM?
How can memory leaks be detected and avoided?
8. Design Patterns and Best Practices
To demonstrate architectural thinking, candidates may be asked:
What is the Singleton pattern and how do you implement it?
Explain the Factory and Observer patterns.
What are SOLID principles in Java programming?
Sample Questions from the Guide
Here are a few samples from "Java Interview Questions and Answers: Your Ultimate Preparation Guide":
1: What is the difference between ‘==’ and .equals() in Java? Ans: == checks reference equality, meaning whether two references point to the same object. .equals() checks logical equality, meaning whether two objects have the same value. For example, two different String objects with the same value will return true using .equals() but false using ==.
2: What is a HashMap, and how does it work internally? Ans: A HashMap stores key-value pairs. It uses a hash function to compute an index where the value should be stored in an array. If multiple keys hash to the same index, Java handles collisions using a linked list or a balanced tree (as of Java 8).
3: How does Java achieve platform independence? Ans: Java code is compiled into bytecode by the Java compiler. This bytecode is platform-independent and can be executed by the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), which is available on multiple operating systems.
How to Use This Guide for Effective Interview Prep
To get the most out of "Java Interview Questions and Answers: Your Ultimate Preparation Guide", follow these steps:
Study the concepts – Don’t just read the answers; understand the reasoning behind them.
Practice coding – Use platforms like HackerRank, LeetCode, or Codeforces to apply Java in real coding problems.
Mock interviews – Simulate real interview scenarios with peers or mentors to practice verbalizing your thoughts.
Build small projects – Implement real-world solutions to solidify your understanding of Java concepts.
Keep learning – Stay up-to-date with Java updates and community discussions to stay ahead of the curve.
Conclusion
Preparation is key to succeeding in a Java interview, and "Java Interview Questions and Answers: Your Ultimate Preparation Guide" is your all-in-one resource for that journey. By mastering the topics covered in this guide, you'll gain the confidence and knowledge needed to impress your interviewers and secure your desired role in the tech industry.
0 notes
Text
Guide to Hire Artificial Intelligence Developers
The Booming Demand for AI Professionals
The artificial intelligence industry has expanded at breakneck speeds over the past few years, presenting new developers with more opportunities than ever. Transitions into careers as AI developers can seem daunting in the presence of the enormity and pace of industry changes. Familiarity with the landscape as well as a thoughtfully planned approach can ease the transition for new hire artificial intelligence developers into a fulfilling yet demanding profession.
Creating Strong Mathematical Foundations
Mathematics is the backbone to building artificial intelligence. Future artificial intelligence developers would be well advised to possess extensive working knowledge of statistics, linear algebra, and calculus. Mathematical concepts are not pedantic principles,these are working tools developers use day in and day out to comprehend algorithms, tune models, and solve complex problems.
The good news is that math is learned in stages. New AI developers need not know each piece of math before starting, yet must be ready to learn on a daily basis. Online tutorials, books, and project learning are excellent vehicles for locking down math concepts as well as learning by doing.
Choosing the Right Programming Languages
Programming skill is necessary for any artificial intelligence developer, but the proper selection of languages will accelerate career growth. Python is currently the most popular language in AI development due to its vast collection of libraries and simplicity of use. R is needed for statistical data and data science, whereas Java and C++ are essential in production environments.
New AI developers will start with Python and later develop language proficiency over time based on career goals. A basic understanding of at least one language and experience with the relative advantages and applications of others is the greatest concern. There is more doing than talking about things that should be done, so project work is essential to programming skill acquisition.
Acquiring Pragmatic Experience Through Projects
Practical experience is in great demand among the upcoming generation of artificial intelligence coders. Side projects demonstrate skill to potential employers and permit learning new tools and techniques. Starting with simple projects and progressing to more complex ones develops confidence and skill.
Good starting projects would include image classification software, sentiment analysis software, or recommendation software. The plan is to choose projects that fit career goals but also cover various aspects of AI development. Documentation of projects and publishing on platforms like GitHub is a way of showcasing abilities to potential employers.
Understand the AI Development Ecosystem
AI development these days relies on an advanced system of platforms, tools, and frameworks. Upcoming developers need to learn popular frameworks like TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit-learn. Clouds such as AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure enable infrastructure for AI development.
Understand this environment to excel better as artificial intelligence professionals and to work with teams. The trick is to start with a blank slate of necessary tools and build up knowledge gradually based on project requirements and professional goals. Practical knowledge with the tools, rather than theory, is more valuable.
Building Domain Knowledge
Effective creators of AI are usually technically proficient with advanced domain expertise. Understanding the specific needs and challenges of industries like medicine, finance, or consumer markets makes developers more effective and useful. Domain knowledge eases the production of the right solution and stakeholder interaction.
New AI developers may wish to specialize in a particular industry or area of interest. Specialization leads to more focused career development and better job opportunities. Reading industry publications, attending conferences, and working on domain projects builds this expertise.
Building a Professional Network
Networking is a critical career progression aspect in artificial intelligence. The AI world is also open to admitting new entrants as well, and most experienced developers are ready to help and impart advice. Professional networks can provide employment, collaboration, and learning avenues.
Potential artificial intelligence creators ought to visit online forums, local meetups, and social media content related to AI. Participating in open-source projects, blogging, and public speaking will make them popular and well-respected within the community.
Staying Current with Industry Trends
The field of AI keeps developing, so artificial intelligence developers are constantly in need of learning. Remaining ahead of the emerging trends and practices requires developers to remain updated by adhering to industry journals, research studies, and industry leaders. Such learning is useful for professional growth and solving problems.
New AI developers have to create learning habits that include reading research papers, keeping an eye on AI blogs, and testing new methods. One does not have to be up to date with everything but keep the ear to the ground on big breakthroughs and know which trends could impact work.
Preparation for the Job Search
Active job searching is needed to get employed in AI development. Early job titles may be "Machine Learning Engineer," "Data Scientist," or "AI Developer." Familiarity with the requirements of these positions is good preparation for applicants.
Successful AI programmers generally start in related careers and then move to AI programming over time. Research, software development, or data analysis would be a solid starting position with networking opportunities. Above all, one needs to be interested in AI programming and be willing to continually learn associated skills.
To become an hire artificial intelligence developers is not a marathon, it's a sprint. With its intricacy and ceaseless revolution, the learning is never over. New developers have to understand this reality and focus on establishing strong foundations and maintaining curiosity and flexibility.
The greatest AI developers are individuals who view obstacles as learning opportunities and are not deterred by unavoidable failure. With persistence, deliberate learning, and experience within the real world, new developers can build successful professional lives within this tech and high-impact field.
0 notes
Text
hi
import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map;
public class FrequencyCounter { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] nums = {2, 3, 2, 5, 3, 2}; Map<Integer, Integer> frequencyMap = new HashMap<>(); for (int num : nums) { frequencyMap.put(num, frequencyMap.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1); } // Print the result for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : frequencyMap.entrySet()) { System.out.println("Number " + entry.getKey() + " appears " + entry.getValue() + " times."); } }
} ////////////////////
rray = [2, 1, 5, 1, 3, 2] target = 8 We’ll find the longest subarray where the sum is ≤ 8.
We use left, right, and sum to control and track the window .int left = 0, sum = 0, max = 0;
left: starting point of our sliding window
sum: running total of the current window
count: total number of valid subarrays we find
for (int right = 0; right < array.length; right++) { Expands the window by moving the right pointer forward. sum += array[right]; while (sum > target) { sum -= array[left]; left++; } max = Math.max(max, right - left + 1); }
/// Inheritance Inheritance allows a class to inherit fields and methods from another class. It supports code reuse and method overriding.
🔹 10. Polymorphism Polymorphism lets you perform the same action in different ways. It includes compile-time (overloading) and runtime (overriding) polymorphism.
🔹 11. Encapsulation Encapsulation binds data and methods together, hiding internal details. It’s achieved using private fields and public getters/setters.
🔹 12. Abstraction Abstraction hides complex implementation details and shows only the essentials. It’s achieved using abstract classes or interfaces.
List allows duplicates, Set allows only unique elements, Map stores key-value pairs. They are part of the Java Collections Framework f
Lambdas enable functional-style code using concise syntax. They simplify the implementation of functional interfaces.
🔹 19. Functional Interfaces A functional interface has exactly one abstract method. Examples include Runnable, Callable, and Comparator.
Stream API processes collections in a functional and pipeline-based way. It supports operations like filter(), map(), and collect()
Heap stores objects and is shared, while Stack stores method calls and local variables. Stack is thread-safe; Heap is managed by the garbage collector.
Immutable objects, like String, cannot be changed once created. They are thread-safe and useful in concurrent applications.
int left = 0, right = array.length - 1; while (left < right) { if (array[left] + array[right] == target) { // Found pair } else if (array[left] + array[right] < target) { left++; } else { right--; } } //////////////////
kafka partitions
List inputList = // input data Map uniqueMap = new HashMap<>();
for (Person person : inputList) { String key = person.name + "_" + person.age;if (!uniqueMap.containsKey(key)) { uniqueMap.put(key, person); // first time seeing this name+age } else {
///
List people = Arrays.asList( new Person("Alice", 30), new Person("Bob", 25), new Person("Charlie", 35) ); // Sort by age using lambda people.sort((p1, p2) -> Integer.compare(p1.getAge(), p2.getAge()));
////////////////
public Person(String name, int age) { this.name = name; this.age = age; }@Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; if (!(o instanceof Person)) return false; Person person = (Person) o; return age == person.age && Objects.equals(name, person.name); } @Override public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(name, age); }
}
/////////// hashCode() is used by hash-based collections like HashMap, HashSet, and Hashtable to find the bucket where the object should be placed.
bject.equals() method compares memory addresses
///
List people = Arrays.asList( new Person("Alice", 30), new Person("Bob", 25), new Person("Charlie", 35) ); // Sort by age using lambda people.sort((p1, p2) -> Integer.compare(p1.getAge(), p2.getAge())); // Print sorted list people.forEach(System.out::println); }
///
0 notes